Why Open Research?
Maximize the potential of your research with Gates Open Research
SUBMIT NOWOpen research (otherwise referred to as 'open science' or 'open scholarship') is a set of principles and practices that prioritize openness, transparency, and collaboration across the entire research cycle. These principles and practices are intended to make all forms of research freely available and useable. Open research is centered on the belief that research can achieve its maximum potential impact when it is disseminated as widely as possible.
Open research aims to open up access to all parts of the research process across academic disciplines. For example:
- methods
- results
- publications
- data
- software
- tools
- peer review
Increased openness facilitates greater collaboration, disseminates knowledge, and supports research integrity. This is also vital to tackling the reproducibility crisis in research. To help ensure Gates-funded researchers have access to a publishing platform that is dedicated to openness, quality, and transparency, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation launched Gates Open Research.
Have questions?
Get in touch with our in-house editorial team who will be happy to support you with any questions you may have!
CONTACT USJoin our mailing list
Be the first to know about calls for papers, exclusive content, researcher stories and more. Sign up to the Gates Open Research mailing list today.
SIGN UP NOWAbout Gates Open Research
The Gates Open Research platform provides Gates-funded researchers with a high-quality venue to publish their research at no cost to themselves. The platform champions open research in every aspect.
Research is rapidly published and freely available following submission and then undergoes open peer review. This open peer review model means that not only are the reviewers’ identities publicly available but also that the peer review reports themselves are published alongside the research. Moreover, Gates Open Research requires that all underlying data associated with research should be shared openly and follow FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) guidelines.
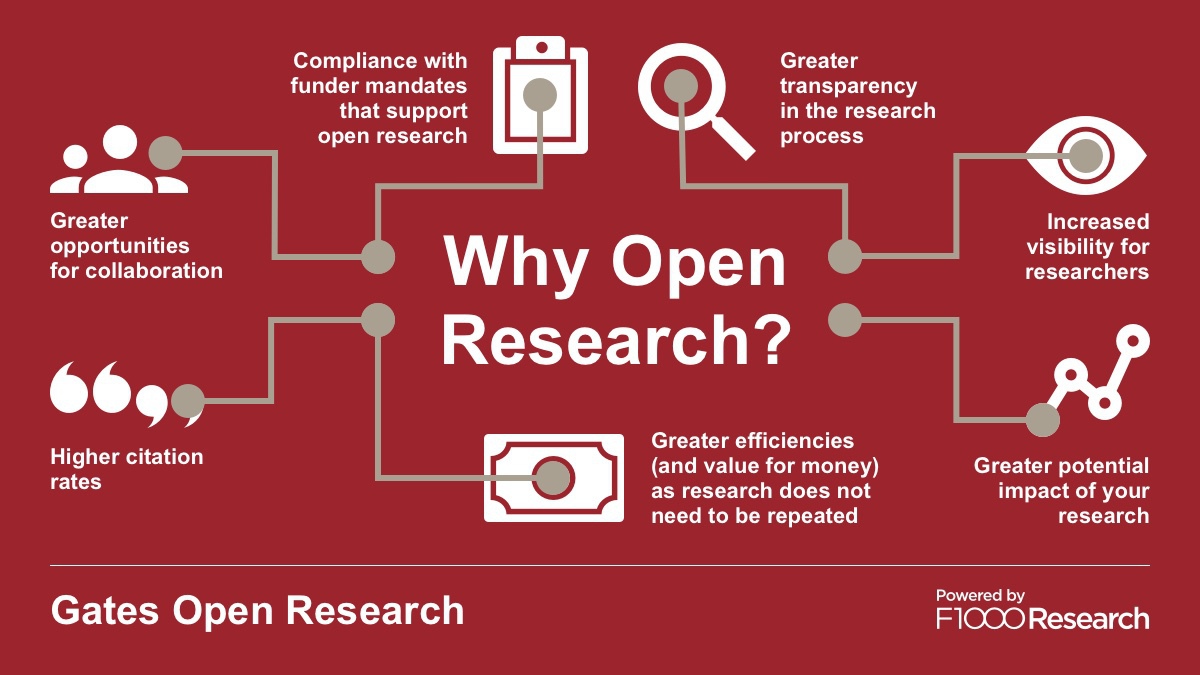
How does open research benefit researchers?
Greater transparency across the whole research cycle leads to greater trust in the published results and improves research integrity.
Higher citation rates due to the open access citation advantage (OACA). Openly available research also tends to receive increased views, downloads, and media attention.
Greater potential impact and recognition for your work—both your own research and peer review. Publish traditional research articles and non-traditional article types, including Data Notes, Method Articles, and more. No matter what form your research takes, it has the potential to make a real-world impact.
Increased visibility for your work by publishing open access, so that anyone, anywhere can discover your research. Plus, publishing on a multi-disciplinary platform like Gates Open Research can help raise your profile within your field of research and across other disciplines.
A streamlined research process as research does not need to be repeated. When you publish openly, code, quantitative data, and qualitative data can be shared, reused, and cited. Others can build upon existing research, which helps to counter the reproducibility crisis.
More opportunities to collaborate are possible when publications and associated data and materials are more widely available.
Compliance with funder mandates and institutional policies that are increasingly supporting open science practices—not to mention meeting the needs of today’s research community.
The 3 central principles of open research
Open research represents a new approach to research creation, recording, and sharing. Open research isn't simply open access. In fact, advocates of open research believe in extending openness to all stages of the research cycle.
While there is a lot to unpack when it comes to understanding open research, it doesn't have to be complicated. Below, we've highlighted three of the most important parts of open science to break down how both research and researchers stand to benefit. Explore the corresponding blog posts for a more in-depth overview.
Open data
What it is
Open data is data that is available for everyone to access, use, and share. For researchers, this refers to any information or materials that have been collected or created as part of your research project. Examples include survey results, gene sequences, software, code, neuro-images, primary source materials, and even audio files. In research, open data practices are also known as ‘data sharing’.
Why it matters
Choosing to publish data openly benefits not only the individual researcher but also the research community and society as a whole. When you publish your data on a platform like Gates Open Research, that data receives a unique DOI and becomes an additional citable research output to add to your portfolio. The wider research community can then verify, use and build upon this data, accelerating the pace of scientific discovery and leading to increased reproducibility.
Furthermore, openly sharing your data can help it to make a real-world impact. Your data could drive innovation in technology, inform evidence-based policy-making, and even lead to public health responses.
Open data myths debunked
If you’re new to the concept of open data, you might be wondering how you separate the facts from the fiction to decide what is right for your research. Here, we debunk some of the most common data sharing myths.
READ NOWOpen peer review
What it is
Open peer review refers to the various possible modifications of the traditional single or double-blind peer review process that together make peer review more transparent.
The Gates Open Research model of open peer review puts transparency center stage. Peer review reports are published alongside the published research, peer reviewers' identities are made known, and authors' responding comments to the reports are visible. The peer review process takes place following publication.
Why it matters
Open peer review makes it easier to trust the research. When peer review reports and the identities of peer reviewers are fully transparent, the possibility of bias is reduced. What's more, studies have shown that open peer review reports tend to be more constructive.
8 things you should know about open peer review
Ready to learn more about open peer review? In this quick-read, we breakdown 8 key aspects of peer review that you might not have come across before.
READ NOWOpen access
What it is
Open access is the free, immediate, online availability of research articles. Open access can be applied to all forms of research outputs - from the traditional research article to conference papers, book chapters, and more.
Why it matters
With unrestricted access to research and research data, we can accelerate further research and create a more equitable system of knowledge. Open access enables research to be more widely disseminated and therefore increases its potential to make a real-world impact. Research that is openly available has also been shown to receive increased views, downloads, and citations.
Open access: taking action to help researchers
Ashley Farley, Program Officer at the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, talks about the foundation’s open research journey, and its first steps into open access to provide its grantees with an alternative to the traditional journal.
READ NOW"The Gates Foundation is dedicated to the belief that all lives have equal value and everyone deserves the opportunity to lead a healthy and productive life. To solve the challenges of the 21st century, we must accelerate open access to high-quality research on health, education, and economic development. Gates Open Research is designed to ensure that the research we fund can be of immediate benefit to society."
Ready to submit?
Read our author guidelines to ensure you’ve prepared your article correctly for submission to Gates Open Research.
READ NOWRead our blog
Visit our blog and discover author interviews, announcements and helpful guides to support you!
VISIT TODAYFAQs
Still have questions about Gates Open Research? Please visit the FAQ page to find out more.
LEARN MORE